Cemented Carbide Plates
- Addtime: 2023-12-07 / View: 1293
Introduction
Tungsten steel plate is one of the many materials of tungsten steel, metallurgical method by powdering, ball milling, pressing, sintering and become, different uses of tungsten steel plate in the WC and Co composition content is not consistent, the use of an extremely wide range of tungsten steel plate, with excellent hardness, high hardness, good wear resistance, high modulus of elasticity, high compressive strength, good chemical stability (resistance to acid, alkali, high temperature oxidation), impact toughness is low, Low coefficient of expansion, thermal conductivity, electrical conductivity and iron and its alloys are similar characteristics. Is also the production of high-temperature parts, wear-resistant parts, anti-shielding parts, corrosion-resistant parts of the excellent material. The use of tungsten steel plate should be specifically selected according to the use of the appropriate material.
Detailed use
Tungsten steel plate has excellent hardness, high hardness, wear resistance, high modulus of elasticity, high compressive strength, good chemical stability (acid, alkali, high temperature oxidation), low impact toughness, low coefficient of expansion, thermal conductivity, electrical conductivity and iron and its alloys are similar to the characteristics of the tungsten steel turning tool has a great deal of superiority, it is rapidly in the industry to be promoted. In just fifty years, due to the use of tungsten steel turning tools, so that the metal cutting speed increased two hundred times, from ten metres per minute to more than two thousand metres. Heat-resistant tungsten steel still retains good elasticity and mechanical strength and is generally used for thicker cuts, interrupted cuts and poor part clamping. Coated tungsten steel is more effective and can be machined to HRC50° in a variety of materials. It has 1~2 times longer service life than normal tungsten steel and excellent impact resistance.
Production process
Powdering → formulated according to the requirements of the use → wet grinding → mixing → crushing → drying → sieving → adding forming agent → drying again → sieving to produce a mixture → granulation → pressing → moulding → sintering → moulding (blanks) → flaw detection and inspection → packaging → warehousing.
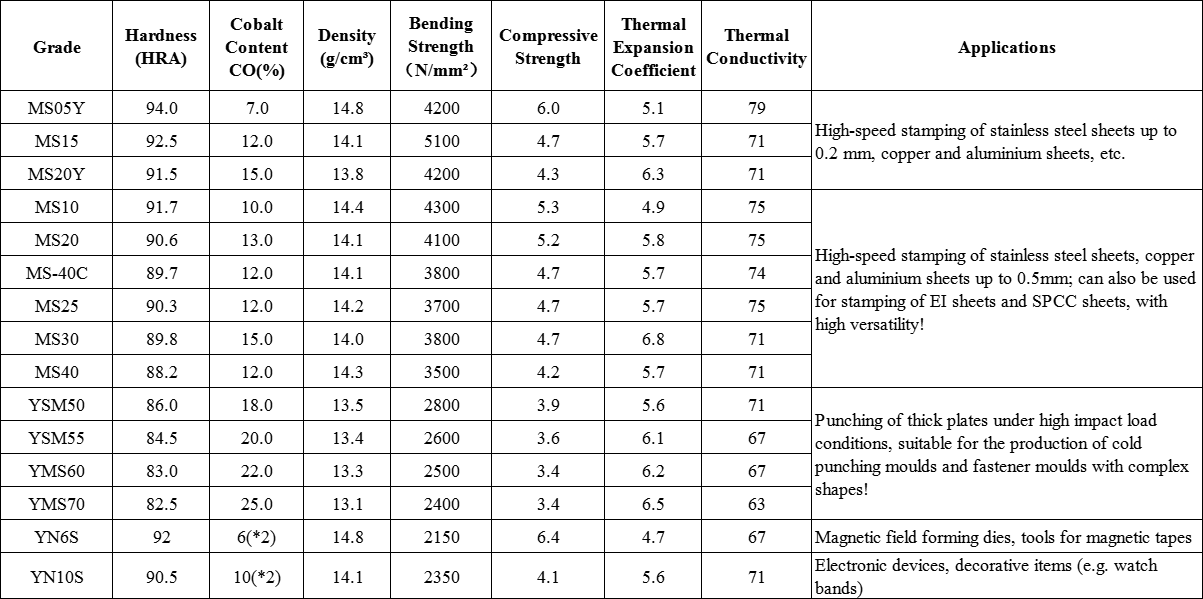
Grades
Moulds and tolerances can be produced according to your requirements, the following are common grades :